Unveiling the Leaders: Top Companies by Generative AI Patents
The field of intelligence is advancing quickly. Patents related to generative AI are leading the way, in this innovative technology. With companies striving to protect their rights to property we now have an understanding of the key players, in this industry. Let’s explore the top companies by generative AI patents, their groundbreaking innovations, and the impact they’re having on the AI landscape.
The Rise of Generative AI Patents
In the years there has been a significant rise, in the issuance of patents for generative AI showcasing the increasing significance of this technology. Between 2014 and 2023 the number of patent families associated with AI surged from 733 to an impressive 14,000. This rapid expansion underscores the competition, among businesses striving to solidify their presence in the AI industry.

China’s Dominance in Generative AI Patents
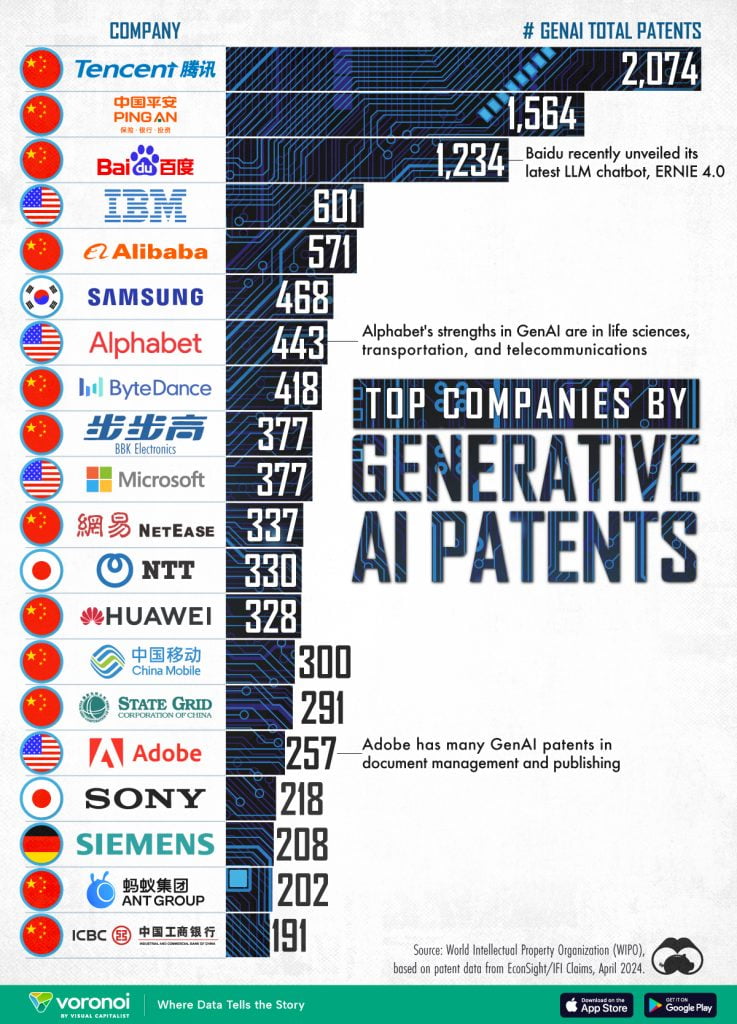
One of the most striking findings is the overwhelming presence of Chinese companies among the top companies by generative AI patents. Tencent and Baidu two players, in the tech industry have obtained a number of patents related to generative AI highlighting Chinas prominent role, in this area. Tencent leads with a 2,074 AI patents, closely followed by Baidu with 1,234 patents.
U.S. Companies Making Their Mark
While Chinese companies dominate the top companies by generative AI patents list, several U.S. firms are making significant strides. IBM, Alphabet (Google) and Microsoft stand out as the companies when it comes to patents related to generative AI. IBMs watsonx platform empowers businesses to. Tailor language models (LLMs) while giving utmost importance to data security and compliance.
On the hand Alphabets AI division has introduced its LLM model named Gemini, which is being incorporated into various products and services. Additionally Microsoft, a supporter of OpenAI. The brains, behind ChatGPT is also playing a role, in shaping the landscape of AI.
The Potential of Generative AI Patents
The competition, for patents in AI isn’t about claiming ownership of ideas; it’s also about influencing the direction of AI advancement. Companies with these patents hold the power to transform sectors, including healthcare, finance, entertainment and more. Advanced generative AI technologies like GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) VAEs (Variational Autoencoders) and LLMs (Large Language Models) are already making waves in fields, like creating images detecting anomalies and enhancing AI.
The Future of Generative AI
As the top companies by generative AI patents continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible, the future of AI looks increasingly promising. Advancements, in technology bring us nearer to a future where AI can address issues boost creativity and enhance our experiences. Yet the swift expansion of AI also prompts discussions, on ethics, privacy and the careful advancement of these technologies.

Final Thought
The top companies by generative AI patents are at the forefront of a technological revolution that has the potential to transform our world. In the quest, for innovation and competition among these companies it becomes evident that generative AI is set to have an impact, on the evolution of artificial intelligence. Observing these industry frontrunners and their pioneering advancements allows us to glean perspectives on the opportunities that await in the future.



